MSc in Computer Vision (1 year, H6J5)
| Description | Scholarships | Programme | Academics |
| Careers | Entry requirements | Contacts | Poster |
News: Queen Mary has been named as the best university in London for student experience link.

Cameras and smartphones are now equipped with advanced Computer Vision technologies that are becoming increasingly sophisticated and effective.
There is great interest in
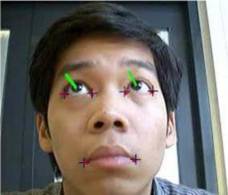
smartphones recognizing their owner,
mood and facial expression using their embedded cameras and other sensors in order to enable real thumbs-up for "liking" on Facebook,
in games played only with body gestures, and in cars that automatically read road signs or do not require the presence of a driver.
This 1-year MSc programme is intended to respond to a growing skills shortage in research and industry for talents with a high level
of training in the analysis and interpretation of images and video. The MSc covers both low-level image processing and high-level
interpretation of videos using state-of-the-art machine learning methodologies. Moreover, it offers high-level training in programming
languages, tools and methods that are necessary for the design and implementation of practical computer vision systems.
The unique set of
skills and knowledge developed in this programme include: theoretical knowledge and practical application of methods in Computer Vision and
Image Processing, programming skills in Matlab or C/C++, data collection and analysis techniques, logical and critical thinking,
and communication and presentation skills.
The programme includes an individual project supervised by one of the leading academics in Computer Vision. Industrial collaborations or commercially focused projects are encouraged and facilitated.
The MSc in Computer Vision offers two MSc fee waivers on a competitive basis.
International Science and Engineering Excellence Awards for the value of either £2,000 or £5,000 per year are available to reward academic achievements, and help to attract the brightest and best students from overseas.
Modules
Students take four modules in Semester 1 (three core and one optional) and four modules in Semester 2 (two core and two optional).
Semester 1
The aim of the course is to give to students an understanding of machine learning methods, including Neural Networks and Clustering algorithms, and to allow them to apply such methods in real world problems. Through lectures and classes that use Matlab, the students will learn several useful algorithms in machine learning and how to use them to analyse data.
Time-frequency transforms are an important tool in the analysis and processing of signals and images. These transforms include the Fourier transform, spectrogram, discrete cosine transform, wavelet transform, and Wigner-Ville distribution. This course aims to introduce transforms and sub-band techniques as a pre-cursor to compression and other applications. It is the first step beyond the fundamentals of Digital Signal processing.
This module equips students with theoretical and empirical knowledge of computer vision principles, from foundations to applications. The module covers core concepts such as light and colour, image formation, filtering, transformations, feature extraction, motion estimation, segmentation, object representation, object detection and tracking. These concepts will be put into practice with several lab exercises. Lectures will also discuss examples of real-world computer vision applications and future prospects of this ever expanding field.
This course is concerned primarily with computer graphics systems and in particular 3D computer graphics. The course will include revision of fundamental raster algorithms such as polygon filling and quickly move onto the specification, modelling and rendering of 3D scenes. In particular, the following topics may be covered: viewing in 2D, data structures for the representation of 3D polyhedra, viewing in 3D, visibility and hidden surface algorithms, illumination computations. Some attention will be paid to human perception of colour and interactive 3D such as virtual reality.
The aim of the course is to introduce students to the paradigm of Parallel Computing, an awareness of its advantages and current limitations and allow the development of practical programming skills in a parallel computing environment. In addition, the students will familiarise with message-passing systems (MPI) as adopted by industry.
Semester 2
Can we interact with a computer, a TV, or a game console beyond a keyboard and mouse or a remote controller, perhaps with natural gesture and/or facial expressions? Computer vision is at the heart of many such question which aims to develop methods that enable a machine to understand images and videos. This module explores more advanced topics in the area of Computer Vision, including image classification, object detection and recognition, facial analysis, motion estimation and human action recognition.
The module aims at providing the knowledge that will enable informed choice about the models, methodologies and technologies that are needed in order to develop applications in emerging areas in the field of Computer Vision. The module will draw heavily on recent advances in the field of machine Learning, thus providing the students with solid knowledge of state-of-the-art methodologies in the domain.
This course gives students a practical introduction to C++ and uses this programming language to examine applications in low-level image processing. Areas covered include image representation, sampling and display, and image transforms and enhancement using point and spatial operations. Image processing methods such as convolution, frequency filtering and image restoration, compression and segmentation, are also considered.
Most computer systems do not sit on desks but are inside machines such as cars and medical devices. This module builds on undergraduate knowledge of operating systems and software engineering to introduce techniques for real-time system development in applications where the performance of the system is critical for safety. Practical work includes use of an ARM Cortex-M4 development board.
Online Social Networks (OSNs) and digital media services such as Facebook, Twitter, Flickr, YouTube are changing the way we interact with the Internet and receive our news, content and recommendations. In this module, the aim is to introduce the concepts around measurement, analysis, usability and privacy aspects of OSNs. The module will bring together a number of studies from different measurement studies on the topic, designs for new systems, and the directions that such networks are taking with the new digital media plans. This module will develop a deep understanding and analysis approach to learning specifically about Social Media and their properties.
The course introduces the students to techniques used in Artificial Intelligence including problem formulation, search, logic, probability and decision theory. The objective of the course is to express problems as search problems and to identify the appropriate techniques for solving them.
This module will cover a broad class of principles needed to develop real-time digital signal processing systems, with a particular focus on the constraints of embedded hardware. Example projects will be drawn mostly from audio, but the principles presented are equally applicable to other domains. Students will develop projects on a development kit containing an ARM Cortex-A8 processor, a platform commonly found in mobile devices.
Semester 3
The individual project supervised by a member of the academic staff may include industrial collaborations or commercially focused activities.
Your skills and knowledge will be valuable in all industries that require intelligent processing and interpretation of image and video. This includes industries in directly related fields, such as multimedia indexing and retrieval (e.g. Google, Microsoft), motion capture (e.g. Vicon), media production (e.g. Sony, Technicolor, Disney), medical imaging, security and defence (e.g. Qinetiq), robotics, and industries in related areas that require good knowledge of machine learning, signal processing and programming.
A number of our academics have common research projects with industrial partners such as Disney, BBC, Technicolor and ST Microelectronics, and take on consultancy work with industry.
Our staff draws on this industry experience to inform and enrich their teaching, bringing theoretical subjects to life. In addition, several of the final year projects are offered in collaboration with research institutes or industrial partners (http://www.bmva.org/visioncompanies).
You will also be ideally placed to pursue further research, including continuing onto PhD studies. We will award two PhD fee waivers for top ranked students in this MSc who desire to continue into our PhD programme.
A good second class honours or above in computer science, electronic engineering, maths, physics or a related discipline.
You should have good knowledge of computer programming, for example using C/C++, Python, Matlab or Java.
For international students we require English language qualifications IELTS 6.5, TOEFL (CBT) 237 or TOEFL (written test) 575.
For questions of administrative nature, please contact
msc-enquiries@eecs.qmul.ac.uk.
For questions about the academic content of the program, please contact
i.patras@qmul.ac.uk using the string [MScVision] in the subject of your email.